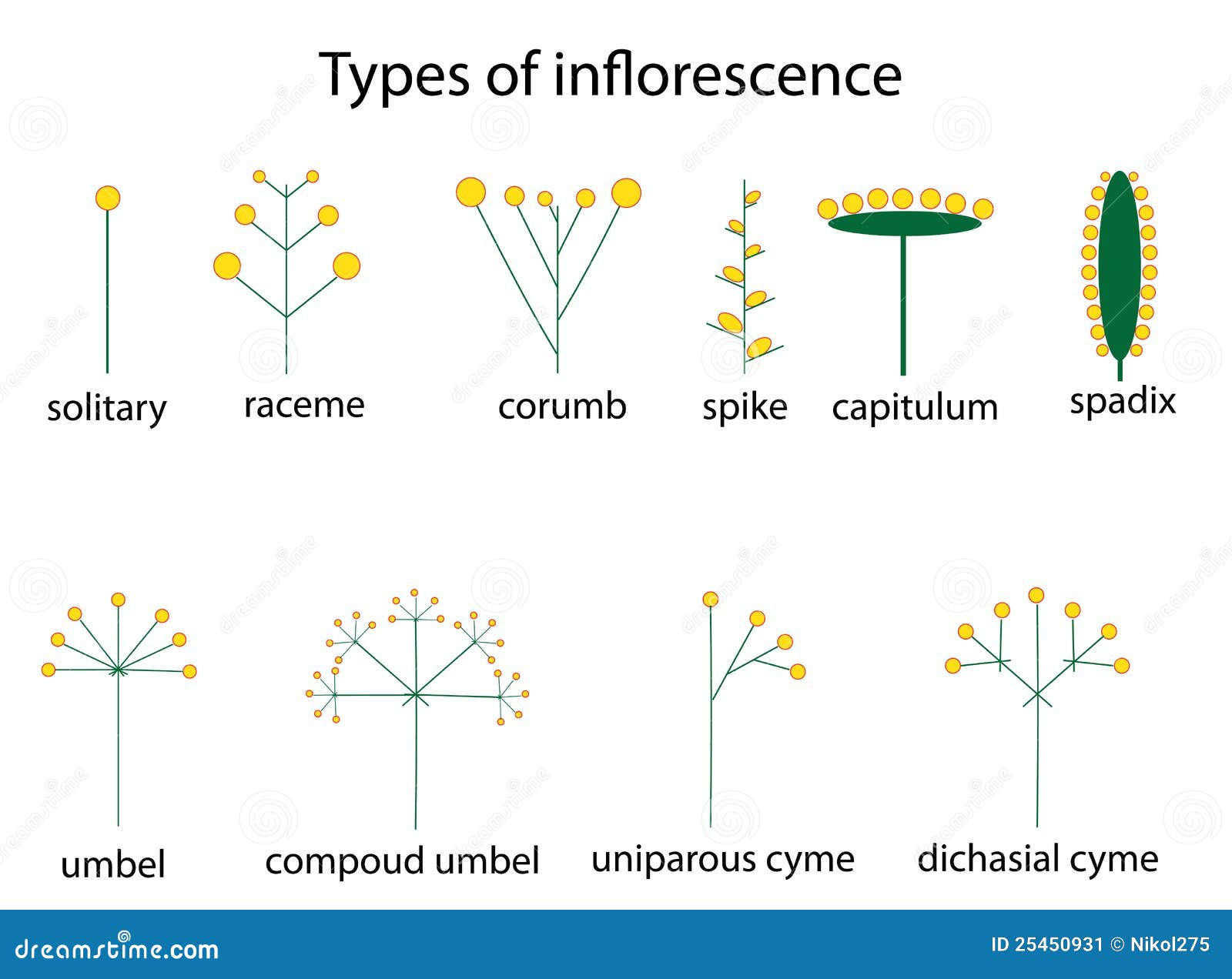
Types of inflorescence stock vector. Image of corumb 25450931
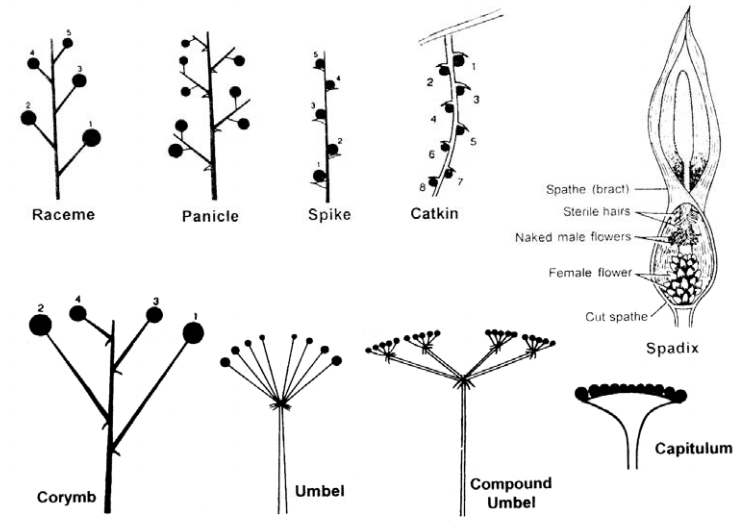
V. FLOWERS ALL ATTACHED AT THE SAME POINT(umbel and head/capitulum) An inflorescence in which several-many pedicellate (stalked) flowers are attached at the same point on a peducnle is called an UMBEL. The umbel is a fairly common inflorescence type. Simple umbels are produced by many clovers (genus Trifolium in Fabaceae, the legume family).

Centripetal arrangement of florets Capitulum/Head InflorescenceTagetes (Fam. Asteraceae) NEET
The types are: 1. Solitary Flowers 2. Racemose Inflorescence 3. Cymose Inflorescence 4. Mixed Inflorescence 5. Special Inflorescence. Type # 1. Solitary Flowers: Flowers occur singly or are separated from other flowers of the same plant by vegetative regions. Solitary flowers are formed by direct transformation of shoot tips into flowers.

Mam, what is umbellate clusters in inflorescence Botany 16482177
When the main axis of raceme is branched and the lateral branches bear the flowers, the inflorescence is known as compound raceme or panicle, e.g., neem (Azadirachta indica), gul-mohar (Delonix regia), etc. The main axis of the inflorescence together with the latest axes, if present, is termed as the peduncle.

The Inflorescence
The composite inflorescence, capitulum, or flower head in Asteraceae assembles multiple flowers into a single, highly compressed structure. It is a very effective reproductive unit and with an apparent selective value, considered to be the key innovation for diversification of this largest family of flowering plants.

Details of capitate inflorescence. (A) Complete inflorescence with... Download Scientific Diagram
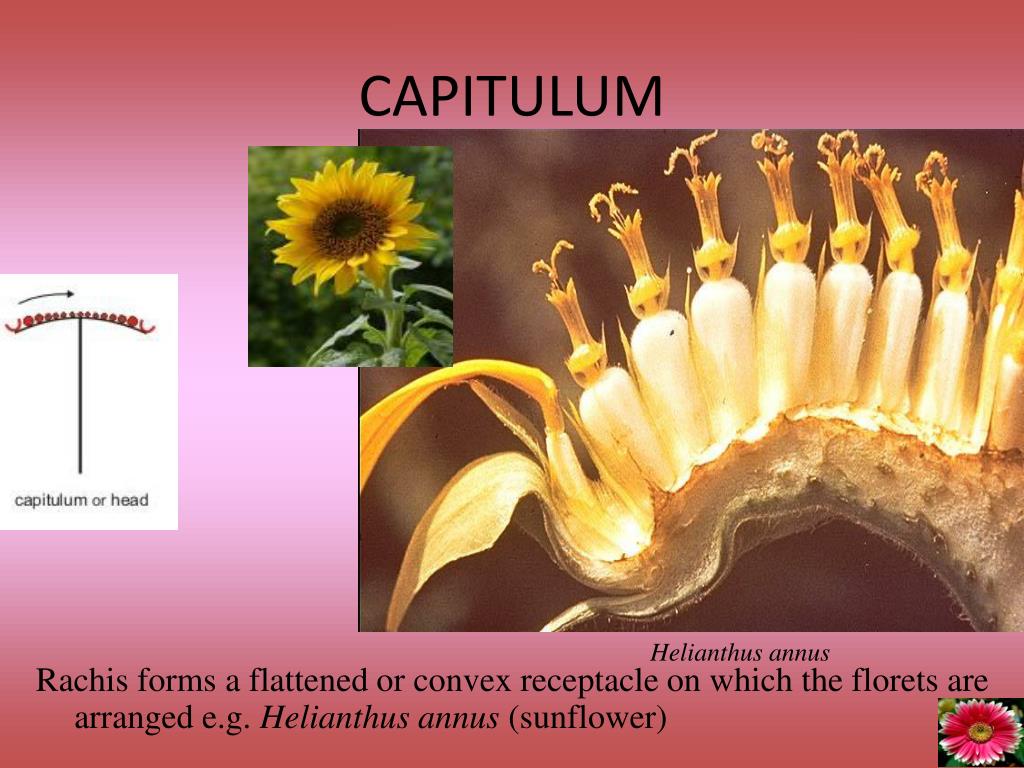
It is an aggregation or cluster of flowers displayed in a specific pattern for a particular plant species. The stem holding this whole reproductive portion of a plant is called a peduncle. The major axis above the peduncle called rachis bears the flowers or secondary branches.
PPT FLOWER ARRANGEMENT ON FLORAL AXIS INFLORESCENCE PowerPoint Presentation ID3779368
capitulum An inflorescence that consists of closely packed flowers or florets which have no stalks and arise on a flattened axis, all at the same level. The capitulum is surrounded or subtended by an involucre of bracts giving it the appearance of a single flower. Capitula are typical of the Compositae. A Dictionary of Plant Sciences MICHAEL ALLABY
Racemose inflorescence Characteristics, Types, Example
Journal Article Floral development and evolution of capitulum structure in Anacyclus (Anthemideae, Asteraceae) M. Angélica Bello , Inés Álvarez , Rubén Torices , Javier Fuertes-Aguilar Annals of Botany, Volume 112, Issue 8, November 2013, Pages 1597-1612, https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcs301 Published: 02 January 2013 Article history PDF Split View

Inflorescence Classification, Types, Significance, Examples
1. Raceme: When peduncle bears many pedicellate flowers in an acropetal manner, e.g., Delphiniumajacis, Veronica, etc. ADVERTISEMENTS: 2. Spike: A raceme with sessile flowers, e.g., Adhatoda vasica, Callistemon, etc.

A Question For The Lone Ranger Page 47 Freethought Forum
A head (capitulum) is a short dense spike in which the flowers are borne directly on a broad, flat peduncle, giving the inflorescence the appearance of a single flower, as in the dandelion ( Taraxacum ). Read More In angiosperm: Inflorescences

AJ. Variations in the inflorescence (capitulum) among different... Download Scientific Diagram
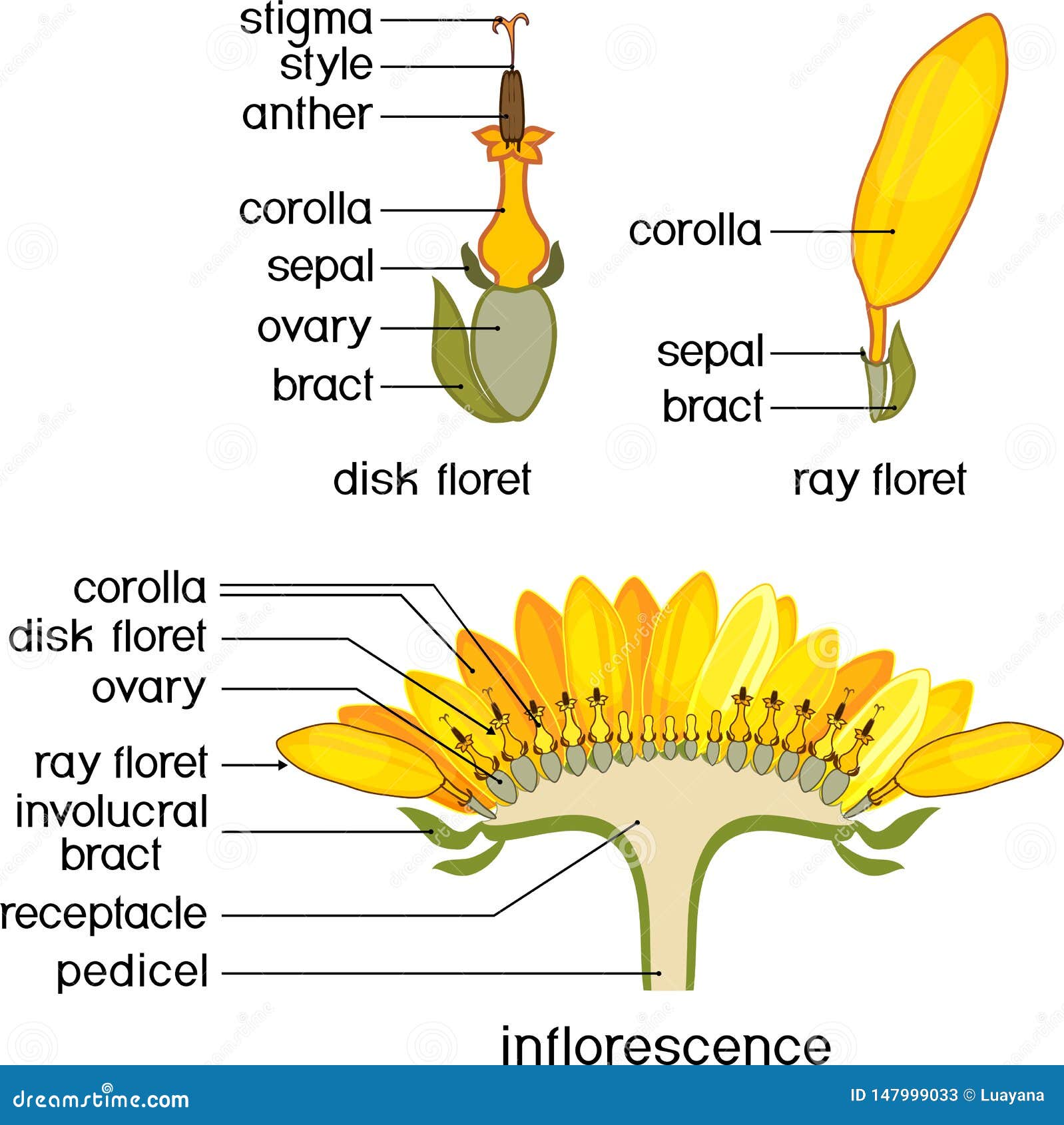
Head (also called a composite or capitulum) Figure 8.4.3 8.4. 3: A dandelion head inflorescence. Each "petal" is actually composed of five fused petals of a single floret. The tube-like structures emerging upward are the styles, each with two curled stigma lobes. Because this inflorescence has no disc flowers, it is called a ligulate head.

The inflorescence in which a cupshaped involucre encloses a single female flower in the centre
The capitulum is a contracted raceme composed of numerous individual sessile flowers, called florets, all sharing the same receptacle. A set of bracts forms an involucre surrounding the base of the capitulum. These are called "phyllaries", or "involucral bracts". They may simulate the sepals of the pseudanthium.

An in situ overhead view of the inflorescence or capitulum of C. cyanus... Download Scientific
Capitulum - Inflorescence axis is flattened to form a receptacle wherein ligulate ray florets and tubular disc florets develop in a centripetal manner. Example - Tridax. Sketch a diagram of a flower of every inflorescence. Label different parts after identification. Position of the ovary is noted corresponding to the floral parts.
Structure Of Flower Of Sunflower In Cross Section. Diagram Of Flower Head Or Pseudanthium. Parts
An inflorescence consisting of a head of small closely packed stalkless flowers or florets arising at the same level on a flattened axis. The whole is surrounded or subtended by an * involucre of bracts and simulates, in appearance and function, a single large flower. The capitulum is typical of members of the family Compositae.

Plant Science (Botany) Multiple Questions and Answers
The inflorescence is the arrangement of flowers in a cluster on the stem of various plants. Each of these arrangements has its specific name. The arrangement helps to facilitate sexual reproduction in various ways. In this article, we will provide detailed information about Inflorescence. Define Inflorescence

Inflorescence Types Racemose, Cymose & Mixed Inflorescence BOTANYYWORLD
10. Capitulum or Head or Anthodium: This is the characteristic inflorescence of the family Compositae. The rachis forms a flattened, more or less convex receptacle on which the florets are arranged in a centripetal order. The whole capitulum is surrounded by an involucre of bracts at the base and each floret usually has its individual scaly bract.

What is inflorescence? Describe Racemose types of inflorescence with a figure. Brainly.in
Spike. Florets are sessile, attached directly to a central axis. Raceme. Similar in structure to a spike, but the florets have pedicels. Panicle. A branched raceme. Use the information above to identify the inflorescence types present in your lab. In the space below, make a sketch of each inflorescence type that will help you make these.